LaTeX templates and examples — Physics
Recent
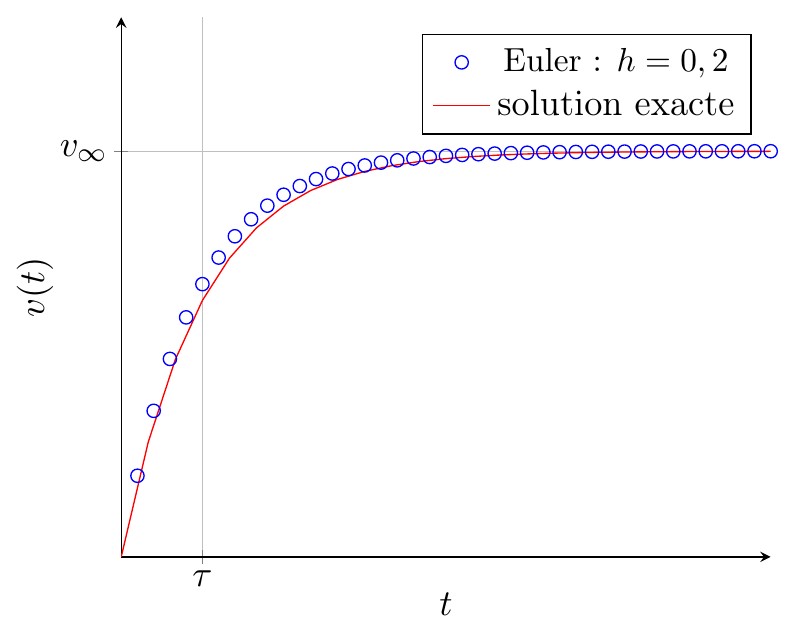
Ce document regroupe les codes TIKZ des figures utilisées pour le cours "traitement numérique des équations différentielles" situé à la page http://femto-physique.fr/analyse_numerique/numerique_C1.php
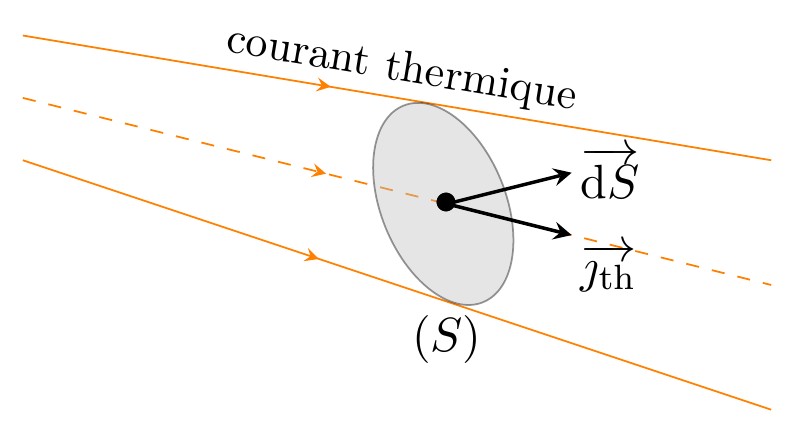
Ce document regroupe les codes TIKZ des figures utilisées pour le cours "TRANSFERTS THERMIQUES" situé à la page http://femto-physique.fr/physique_statistique/phystat_C5.php
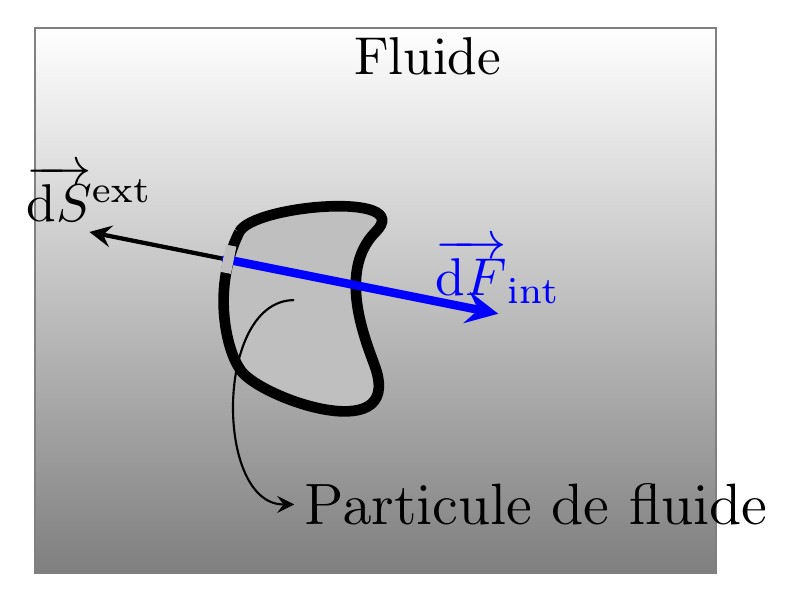
Ce document regroupe les codes TIKZ des figures utilisées pour le cours "DYNAMIQUE DES FUIDES PARFAITS" situé à la page http://femto-physique.fr/mecanique_des_fluides/mecaflu_C2.php
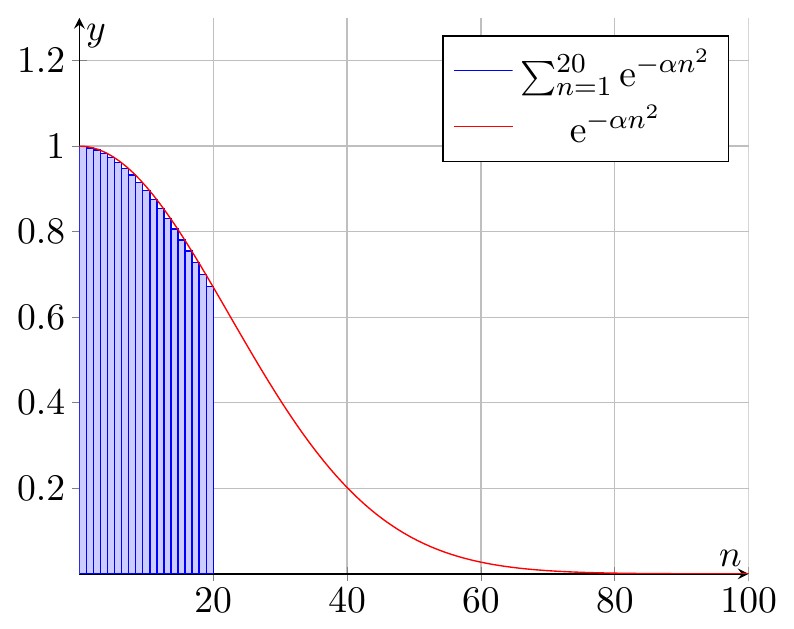
Ce document regroupe les codes TIKZ des figures utilisées pour le cours "Le gaz parfait" situé à la page http://femto-physique.fr/physique_statistique/phystat_C3.php

Thermal wave phenomenon is observed is thin metallic rod by application of periodic heating. In this way, it is demonstrated that there is no wave nature in these improperly called thermal waves by showing that they do not transport energy and its propagation properties can be used to determine the thermal diffusivity of the material.
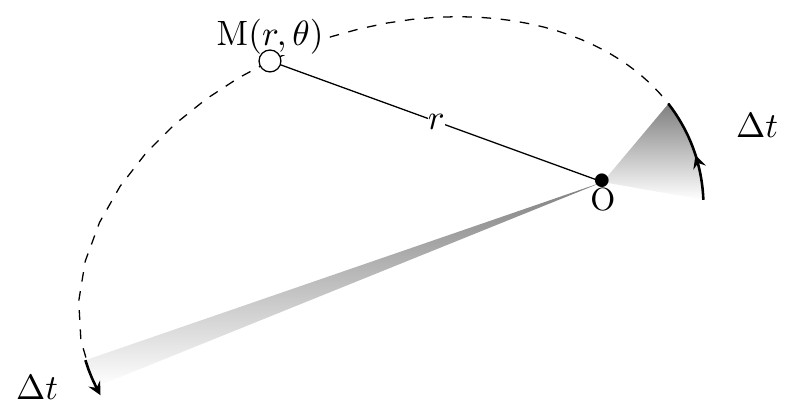
Codes TikZ des figures du cours "Mouvememnts à force centrale" situé à l'adresse : http://www.femto-physique.fr/mecanique/meca_C7.php
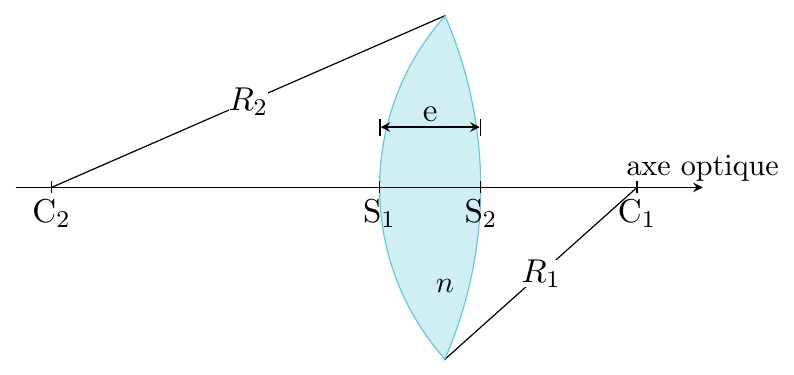
Ce document regroupe les codes TIKZ des figures utilisées pour le cours "Les lentilles minces" situé à la page: http://femto-physique.fr/optique_geometrique/opt_C3.php

The aim of this laboratory work is to design a strut/bracket assembly for aircrafts. Experiments are carried out to determine mechanical properties of certain materials.The material chosen is Mild Steel. Given the possible condition experienced by the material and the safety factor, the dimensions for the designs of the strut/bracket assembly for aircrafts are obtained to avoid failure by yield or fracture. The diameter of the pin, d ,which is subjected to shear stress should be larger than 14.56mm. The diameter of the rod, D, should be larger than 12.74mm. The thickness of the rod would be 10mm.

To get the correct answer one must ask the correct question. In the field of Quantum Gravity the question has been how do we quantize General Relativity or derive a quantum theory which becomes General Relativity at low energies. Observing that Quantum Field Theory was the result of making Quantum Mechanics into a relativistic theory, I asked myself why not make QFT obey the principles of GR? I answered this question with a model I call Relativization. In a series of three papers I presented an answer to this alternative question which gives finite results for everything from black holes to particle physics. Presented at the April meeting of the American Physical Society
\begin
Discover why over 25 million people worldwide trust Overleaf with their work.